The Benefits of Leasing vs. Buying for Auto Dealers presents a compelling analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of each option for both dealerships and customers. While buying a vehicle offers the security of ownership and potential long-term financial benefits, leasing provides flexibility, lower upfront costs, and can attract a broader customer base. This article delves into the financial implications, ownership dynamics, maintenance considerations, and customer preferences associated with both leasing and buying, highlighting the unique benefits each option presents to auto dealers.
Understanding the intricacies of leasing and buying can empower dealers to make informed decisions that align with their business goals and cater to the evolving needs of their customers. By exploring the financial aspects, ownership implications, and customer preferences associated with each option, dealers can develop strategies that optimize sales, profitability, and customer satisfaction.
Financial Considerations
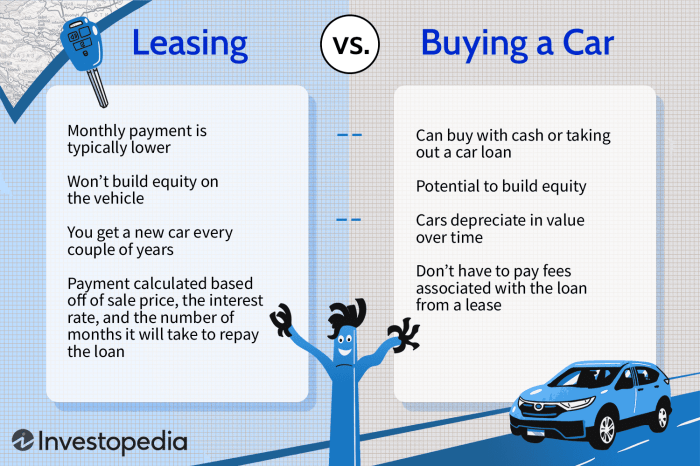
When deciding between leasing and buying a vehicle, it’s crucial to carefully analyze the financial implications of each option. Understanding the upfront costs, monthly payments, and long-term financial commitments associated with each approach can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals.
Upfront Costs
The initial expenses associated with leasing and buying a vehicle differ significantly.
- Leasing: Typically involves a lower upfront cost compared to buying. This is because you’re essentially renting the vehicle for a set period, and the lease agreement covers the depreciation of the vehicle during that time. You’ll usually pay a security deposit, first month’s lease payment, and potentially a down payment, but these amounts are generally less than the down payment required for a car loan.
- Buying: Requires a larger upfront investment. You’ll need to pay a down payment, which can be a significant portion of the vehicle’s price, as well as any applicable taxes and registration fees. Additionally, you might need to factor in the cost of financing the remaining balance through a car loan.
Monthly Payments
The monthly payments for leasing and buying a vehicle can also vary considerably.
- Leasing: Typically results in lower monthly payments than buying. This is because you’re only paying for the depreciation of the vehicle during the lease term, not the full purchase price. Lease payments are usually calculated based on the vehicle’s residual value, which is the estimated market value at the end of the lease term.
- Buying: Involves higher monthly payments due to financing the entire purchase price over a longer period. The loan amount, interest rate, and loan term all impact the monthly payment.
Long-Term Financial Implications
The long-term financial implications of leasing and buying a vehicle are distinct.
- Leasing: Provides flexibility and lower monthly payments, but you won’t own the vehicle at the end of the lease term. You’ll need to return the vehicle to the dealership or pay a buyout price to keep it. This means you’ll be making lease payments for a set period, after which you’ll have no equity in the vehicle.
- Buying: Offers the benefit of owning the vehicle outright after you’ve paid off the loan. This gives you the freedom to sell the vehicle, trade it in, or keep it for as long as you want. However, buying a vehicle can result in higher upfront costs and monthly payments.
Tax Benefits
Leasing can offer certain tax benefits, particularly for businesses.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) considers lease payments as business expenses, which can be deducted from taxable income.
This can result in tax savings for businesses that lease vehicles for commercial purposes. However, it’s important to consult with a tax professional to determine the specific tax benefits associated with leasing in your situation.
Flexibility and Ownership
Leasing and buying a vehicle present distinct approaches to ownership and flexibility, each catering to different needs and preferences. While buying offers complete ownership, leasing provides greater flexibility in terms of vehicle upgrades and financial management. Understanding the implications of both options is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your individual circumstances.
Ownership Implications, The Benefits of Leasing vs. Buying for Auto Dealers
Leasing and buying differ significantly in terms of ownership. When you buy a car, you become the legal owner from the moment you complete the purchase. This means you have full control over the vehicle, including the right to sell, modify, or keep it indefinitely.
Leasing, on the other hand, grants you the right to use the vehicle for a predetermined period, typically two to five years. You make monthly payments for the privilege of driving the car, but you do not own it. At the end of the lease term, you have three options:
- Return the vehicle to the dealership, assuming you have adhered to the terms of the lease.
- Purchase the vehicle at a predetermined price, known as the residual value.
- Lease a new vehicle.
Customization and Modifications
Customization and modifications are generally more restricted with leased vehicles. While minor cosmetic changes are typically allowed, major modifications, such as engine swaps or bodywork alterations, are often prohibited in lease agreements. This is because the lessor wants to ensure the vehicle remains in good condition and retains its resale value.
Buying a car gives you complete freedom to customize and modify it to your liking. You can personalize the interior, upgrade the exterior, or even perform extensive engine modifications. However, it’s important to note that some modifications may affect the vehicle’s resale value.
Resale Value of Leased Vehicles
The resale value of a leased vehicle is generally lower than a comparable car that has been owned outright. This is because leased vehicles are typically driven for a shorter period and may have more wear and tear.
However, leased vehicles are often maintained to a higher standard due to the lease agreement’s terms. This can help to preserve the vehicle’s value and make it more appealing to potential buyers.
Maintenance and Repair
When deciding between leasing and buying a vehicle, maintenance and repair costs are a crucial factor to consider. The responsibilities and potential expenses associated with these aspects can vary significantly depending on whether you choose to lease or purchase.
Deciding whether to lease or buy a car can be a significant decision for dealerships, impacting their inventory management, customer offerings, and overall profitability. Understanding the financial implications of each option is crucial, and a deep dive into Understanding Auto Financing Options for Dealerships can provide valuable insights.
By analyzing leasing and buying options through this lens, dealerships can make informed choices that align with their business goals and optimize their financial performance.
Lease Agreement Responsibilities
Lease agreements typically Artikel specific responsibilities for maintenance and repairs. While the exact terms can vary, leaseholders are generally responsible for:
- Regular Maintenance: This includes tasks such as oil changes, tire rotations, and fluid checks. These services are usually performed at authorized dealerships or service centers to maintain the vehicle’s condition and ensure it meets the lease agreement’s requirements.
- Wear and Tear: Lease agreements often include clauses regarding wear and tear. You’ll be responsible for addressing any damage or deterioration beyond normal use, such as scratches, dents, or excessive tire wear.
- Covered Repairs: Most lease agreements cover major repairs related to mechanical or electrical issues during the lease term. However, these repairs must be performed at authorized service centers, and you’ll likely need to pay a deductible for each covered repair.
Warranty Coverage
The warranty coverage for leased and purchased vehicles differs in several key aspects:
- Manufacturer’s Warranty: Both leased and purchased vehicles are typically covered by the manufacturer’s warranty for a specific period or mileage. This warranty covers defects in materials and workmanship and is usually transferable to subsequent owners if the vehicle is sold.
- Lease-Specific Warranty: Some lease agreements include additional warranty coverage beyond the manufacturer’s warranty. This extended coverage may protect against certain wear and tear items or provide additional protection against unexpected repairs. However, these warranties are usually specific to the lease agreement and may not be transferable if you purchase the vehicle at the end of the lease.
Cost of Repairs
The cost of repairs for leased and purchased vehicles can differ significantly. Here’s a breakdown of the potential costs:
- Leased Vehicles: While you’re typically responsible for regular maintenance and wear and tear, major repairs are often covered by the lease agreement. However, you’ll likely need to pay a deductible for each covered repair. In addition, you may be charged for exceeding the allowed mileage or for excessive wear and tear, which can impact the overall cost of repairs.
- Purchased Vehicles: When you purchase a vehicle, you’re responsible for all maintenance and repairs, including major repairs. While the manufacturer’s warranty covers certain issues, you’ll be responsible for the cost of repairs once the warranty expires. However, you have the freedom to choose where to have your vehicle repaired and can potentially save money by using independent mechanics.
Unexpected Repair Expenses
Unexpected repair expenses can occur with both leased and purchased vehicles. However, the financial impact can be different:
- Leased Vehicles: While major repairs are often covered under the lease agreement, unexpected repairs outside of the covered scope can be costly. You may be responsible for the full cost of these repairs, and exceeding the allowed mileage or incurring excessive wear and tear can lead to additional charges at the end of the lease.
- Purchased Vehicles: With a purchased vehicle, you’re responsible for all repair costs, including unexpected ones. While you can potentially save money by using independent mechanics or negotiating prices, the financial burden of unexpected repairs rests entirely on you. However, you have the flexibility to decide whether to repair or replace the vehicle based on your budget and needs.
Dealer Perspective
From a dealer’s perspective, leasing presents a compelling business model with numerous advantages. Leasing can boost sales volume, generate higher profit margins, and attract a wider customer base. However, managing a lease program comes with its own set of challenges.
Increased Sales Volume
Leasing can significantly contribute to increased sales volume for auto dealers. By making vehicles more affordable and accessible, leasing attracts customers who might not be able to afford a traditional purchase. Lower monthly payments and shorter lease terms can entice customers who prefer flexibility and the latest models. Furthermore, leasing can help dealers move slow-moving inventory, as customers are more likely to lease a vehicle they might not purchase outright.
Higher Profit Margins
Leasing can generate higher profit margins for dealers compared to traditional sales. Dealers can often earn a higher markup on leased vehicles, as they retain ownership and control over the vehicle’s residual value. Additionally, dealers can generate revenue from lease fees, maintenance packages, and other ancillary services.
Challenges of Managing a Lease Program
While leasing offers significant advantages, managing a lease program comes with its own set of challenges. Dealers must carefully manage residual values, as these determine the profitability of each lease. Accurate residual value estimates are crucial to avoid losses or unexpected expenses. Additionally, dealers need to establish a robust system for tracking lease payments, monitoring vehicle condition, and managing lease terminations.
Customer Preferences: The Benefits Of Leasing Vs. Buying For Auto Dealers
Understanding customer preferences is crucial for auto dealers to effectively market and sell vehicles, whether through traditional sales or leasing options. This section explores the factors influencing customer decisions, demographics of typical lease customers, common reasons for choosing leasing, and the potential for customer satisfaction with leasing.
Factors Influencing Customer Preferences
Various factors influence customer preferences for leasing or buying a vehicle. These factors include:
- Financial Situation: Leasing is often more affordable than buying, especially for those with limited upfront capital or seeking lower monthly payments.
- Driving Habits: Customers who drive fewer miles or prefer to upgrade their vehicles frequently may find leasing more advantageous.
- Lifestyle: Leasing offers flexibility for those who value mobility and desire the latest vehicle models.
- Personal Values: Some customers prioritize ownership and the long-term benefits of owning a vehicle, while others prefer the convenience and flexibility of leasing.
Demographics of Typical Lease Customers
Lease customers typically belong to certain demographics:
- Younger Generation: Millennials and Gen Z are more likely to lease vehicles due to their preference for flexibility and affordability.
- Urban Dwellers: Residents of densely populated areas may favor leasing due to limited parking space and the convenience of not owning a vehicle.
- Professionals: Individuals with higher incomes may choose leasing for its convenience and the ability to drive a luxury or high-end vehicle without a significant upfront investment.
Reasons for Choosing Leasing
Customers choose leasing for several reasons:
- Lower Monthly Payments: Leasing often results in lower monthly payments compared to financing a purchase, making it more affordable for budget-conscious consumers.
- Flexibility and Convenience: Leasing offers the flexibility to upgrade to a newer model every few years without the hassle of selling an old vehicle.
- Predictable Costs: Lease agreements typically include fixed monthly payments, making it easier to budget for vehicle expenses.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Some lease agreements include maintenance coverage, reducing the burden of repair and maintenance costs.
Customer Satisfaction with Leasing
Customer satisfaction with leasing can vary depending on factors such as the lease terms, vehicle reliability, and the dealership’s customer service. However, leasing can offer several benefits that contribute to customer satisfaction:
- Driving a New Vehicle: Leasing allows customers to drive a newer model vehicle every few years, providing a sense of satisfaction and novelty.
- Reduced Financial Risk: Leasing minimizes the risk of depreciation, as the lessee is not responsible for the vehicle’s value at the end of the lease term.
- Convenience and Flexibility: The ease of upgrading to a newer model and the flexibility to terminate the lease early (with potential penalties) contribute to customer satisfaction.
Conclusive Thoughts

Ultimately, the decision of whether to lease or buy a vehicle depends on a variety of factors, including individual financial circumstances, driving habits, and personal preferences. By carefully considering the advantages and disadvantages of each option, both dealers and customers can make informed choices that best suit their needs. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the choice between leasing and buying will likely remain a critical consideration for auto dealers seeking to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
Understanding the benefits of leasing vs. buying for auto dealers is crucial for maximizing profitability and customer satisfaction. A key aspect of success is building a strong brand that resonates with your target audience, which can be achieved through effective marketing strategies, excellent customer service, and a commitment to ethical practices.
Learn more about how to build a strong brand for your auto business by visiting How to Build a Strong Brand for Your Auto Business , and then leverage that strong brand to highlight the unique advantages of leasing or buying for your customers.